SpringMVC请求处理及组件分析
总览
在SpringMVC启动分析一节,
我们聊到DispatcherServlet这一SpringMVC的核心处理器的继承关系。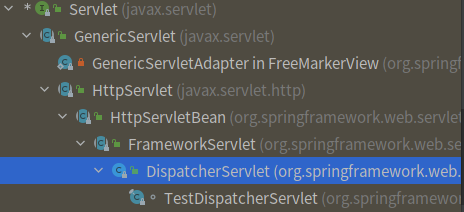
DispatcherServlet作为Servlet的一个实现, 我们从Servlet容器(Tomcat、Jetty等)的角度看看他们处理HTTP请求时 是如何调用Servlet实现的。
首先会调用到Servlet的service方法。
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)
throws ServletException, IOException;
DispatcherServlet的父类调用源码不粘贴在此处分析(因为有点累赘),
实际上,是HttpServlet实现了service方法,并分发到doGet、doPost、doPut、doDelete等方法,
然后其子类FrameworkServlet实现了这些方法,并最终调用自身的抽象doService方法protected abstract void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws Exception;
而DispatcherServlet实现了doService方法,然后来到了SpringMVC的处理逻辑。
doService方法会设置一些框架对象,WebApplicationContext等到request属性中,接着 我们看看核心方法doDispatch:
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
//1 给需要异步处理的请求使用,一般是给SPI使用,不是通用管理器
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
//2 使用multipartResolver检查并解析出文件数据封装到MultipartFile并加到request属性中
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
//3 找到请求处理的HandlerExecutionChain,请求处理链,里面包含了interceptror
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
//4 调用HandlerAdapter.supports(handler)方法去找到适合的HandlerAdapter
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
//5. 调用HandlerExecutionChain的applyPreHandle方法
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
//6. HandlerAdapter调用HandlerExecutionChain里的handler(一般定义的spring mvc controller的handler类型是InvocableHandlerMethod)
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
//7. 调用HandlerExecutionChain的posthandle,即调用Interceptor的postHandle
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
//8. 如果了发生异常,则执行handlerExceptionResolvers集合的resolveException,最后triggerAfterCompletion
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
没错,上面就是SpringMVC的核心主流程了~
可是我们不禁会问,
- 我们写的Controller是如何被加载进SpringMVC的又是怎样在HTTP请求中被匹配到的呢?
- Controller方法的参数是如何从HTTP字符串中转换出来的呢?
- 如何自定义参数处理器呢?
- ……
嗯,不急,接下来继续分析。
DispatcherServlet如何定位和处理Controller
RequestMappingHandlerMapping初始化(Controller方法是如何被加载?)
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping,
看名字它是一个处理@RequestMapping并转换成请求->Handler的mapping的类。
首先,我们来看看该类初始化。
由于该类实现了InitializingBean接口,所以在初始化时会调用afterPropertiesSet这个方法。
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
//初始化handlerMethods
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
//这是工厂方法,目前没作用
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
//找到Controller和RequestMapping的标注,作为handler。
@Override
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
processCandidateBean方法中调用的detectHandlerMethods里面有三步:
- getMappingForMethod(method, Class) 创建RequestMappingInfo,供请求时匹配HandlerMethod
- AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod 过滤能够调用的,排除private、static或Spring代理方法。
- registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping) 用MappingRegistry创建HandlerMethod
RequestMapping方法寻找和controller调用过程
我们来看核心方法AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request)的分析。
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
//和@RequestMapping定义的没有变量的那些路径,做直接匹配
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
//通过RequestMappingInfo.getMatchingCondition,生成能够匹配上的RequestMappingInfo
//返回Match对象(匹配结果)
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// 所有mapping都调用一遍,看是否能匹配上
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
//按RequestMappingInfo.compareTo中定义的匹配逻辑去做比对,选出优先级最高的Match对象(RequestMapping)
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.handlerMethod);
//设置一些成功匹配(mapping)的匹配信息到request Attr中
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
//返回HandlerMethod
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
以上就是HandlerMethod的匹配过程,最终在DispatcherServlet中, HandlerMethod会被包装到HandlerExecutionChain中。
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter将会调用
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception
我们来看看核心方法invokeHandlerMethod的调用handlerMethod过程。
重点留意:HandlerMethodArgumentResolver、HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler的调用。
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
//1 封装一个Servlet请求的请求变量
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try {
//2 获取WebDataBinderFactory这一创建 WebDataBinder 的工厂
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
//3
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
//4 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod拓展了InvocableHandlerMethod,并支持了HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler的处理,
// InvocableHandlerMethod支持了HandlerMethodArgumentResolver的处理
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
//5 设置HandlerMethodArgumentResolver集合
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
//6 设置HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler集合
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
//7 初始化ModelAndViewContainer并处理@SessionAttribute和@ModelAttribute的方法(现在前后分离的大环境下,一般很少用到)
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);
asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor);
asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors);
asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors);
if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) {
Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult();
mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0];
asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult();
LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> {
String formatted = LogFormatUtils.formatValue(result, !traceOn);
return "Resume with async result [" + formatted + "]";
});
invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result);
}
// 8 invocableMethod处理请求并调用我们标注的对应的requestMapping方法
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
finally {
webRequest.requestCompleted();
}
}
接下来我们来看ServletInvocableHandlerMethod如何处理handlerMethod
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
//8.1 转换请求参数并调用方法
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
//省略
//8.2 处理并转换返回结果
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
//省略
}
上面的8.1方法调用中,转换参数会通过HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite集合调用HandlerMethodArgumentResolver的各个实现类的两个方法
supportsParameter(MethodParameter)通过这个方法找到支持转换当前方法参数的HandlerMethodArgumentResolverresolveArgument(MethodParameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer, NativeWebRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory)进行请求参数->方法参数对象的转换。
那么我这里列举下常见的不同方法参数的对应HandlerMethodArgumentResolver(handler方法参数解析器):
- @RequestParam 注解对应的是RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver解析器(作用不止于此)。
- @PathVariable 注解对应的是PathVariableMapMethodArgumentResolver解析器。
- @RequestBody 注解对应的是RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor解析器。
- 没有注解的model 对应使用ModelAttributeMethodProcessor解析器。
- 带@RequestParam注解的Map 对应使用RequestParamMapMethodArgumentResolver解析器。
- @RequestAttribute 对应的是RequestAttributeMethodArgumentResolver解析器。
- @RequestPart 注解对应的是RequestPartMethodArgumentResolver解析器。
结果解析
在上面分析ServletInvocableHandlerMethod的调用中,简单说到
8.2 处理并转换返回结果
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
会通过HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerComposite集合调用HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler的两个方法:
supportsReturnType(MethodParameter returnType)通过这个方法找到能够处理当前调用返回值的HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerhandleReturnValue(@Nullable Object returnValue, MethodParameter, ModelAndViewContainer, NativeWebRequest) throws Exception;处理对应returnValue。
同样,我列举下常见的HandlerMethodArgumentResolver(返回值解析器):
- @ResponseBody 注解对应的是RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor解析器。
同时,阅读源码时,注意这几个类:
- RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor
- RequestResponseBodyAdviceChain
- HttpMessageConverter
异常处理
初始化及作用
无论是从DispatcherServlet.properties文件初始化还是通过@EnableWebMvc或者Spring Boot中自加载的WebMvcConfigurationSupport初始化DispatcherServlet 策略对象,一般都会加载这三个默认的HandlerExceptionResolver子类:
- ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver 处理@ExceptionHandler注解
- ResponseStatusExceptionResolver 处理controller抛出的带@ResponseStatus注解的Exception
- DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver 处理SpringMVC的一些框架异常
一般ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver这一处理器足够我们使用,不过如果我们有定制需求,
可以通过WebMvcConfigurer挂载自己拓展的HandlerExceptionResolver。
调用点
在本文开始,分析DispatcherServlet的处理请求中,我们分析到如下语句,做了简单介绍:
//8. 如果了发生异常,则执行handlerExceptionResolvers集合的resolveException,最后triggerAfterCompletion
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
上面的方法里面的实现比较简单,就是按顺序调用DispatcherServlet的HandlerExceptionResolver集合的resolveException方法,如果有返回值就停止调用并返回。
额外说说,ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver的调用,
- 调用shouldApplyTo方法看当前ExceptionResolver能否处理当前Handler
- 调用doResolveHandlerMethodException处理ExceptionHandler
- 创建ServletInvocableHandlerMethod
- 寻找当前Handler的@ExceptionHandler方法,不存在的话,寻找@ControllerAdvice(ControllerAdviceBean)
- 最终都是通过ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver去找到对应的调用方法
- 把对应方法包装到ServletInvocableHandlerMethod供调用
- 设置对应的HandlerMethodArgumentResolver和HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler供异常处理方法的入参和出参处理
- 执行调用
- 创建ServletInvocableHandlerMethod
核心方法ServletInvocableHandlerMethod getExceptionHandlerMethod(HandlerMethod, Exception)。
拓展:Servlet容器的异常处理
Servlet容器(Tomcat、Jetty等)有一个Error page的概念。Error page能够将返回错误状态码的请求重定向到我们定义的error page。
这里使用Tomcat做举例:
- 在web.xml中可以这样定义error page:
<!--errorpage handler --> <error-page> <error-code>404</error-code> <location>/WEB-INF/jsp/errors/error.jsp</location> </error-page> <error-page> <error-code>500</error-code> <location>/WEB-INF/jsp/errors/error.jsp</location> </error-page> <error-page> <error-code>400</error-code> <location>/WEB-INF/jsp/errors/error.jsp</location> </error-page> - 在embed Tomcat中使用
org.apache.catalina.Context的void addErrorPage(ErrorPage errorPage);方法添加error page。
Spring Boot默认定义的Error Page
在Spring Boot中,Spring Boot为我们默认定义了一个全局错误处理error page(路径是/error),它在不同content-type下会返回HTML或者JSON信息。
核心配置类org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration。
//错误controller
public BasicErrorController basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes) {
return new BasicErrorController(errorAttributes, this.serverProperties.getError(),
this.errorViewResolvers);
}
//错误页注册器
public ErrorPageCustomizer errorPageCustomizer() {
return new ErrorPageCustomizer(this.serverProperties, this.dispatcherServletPath);
}
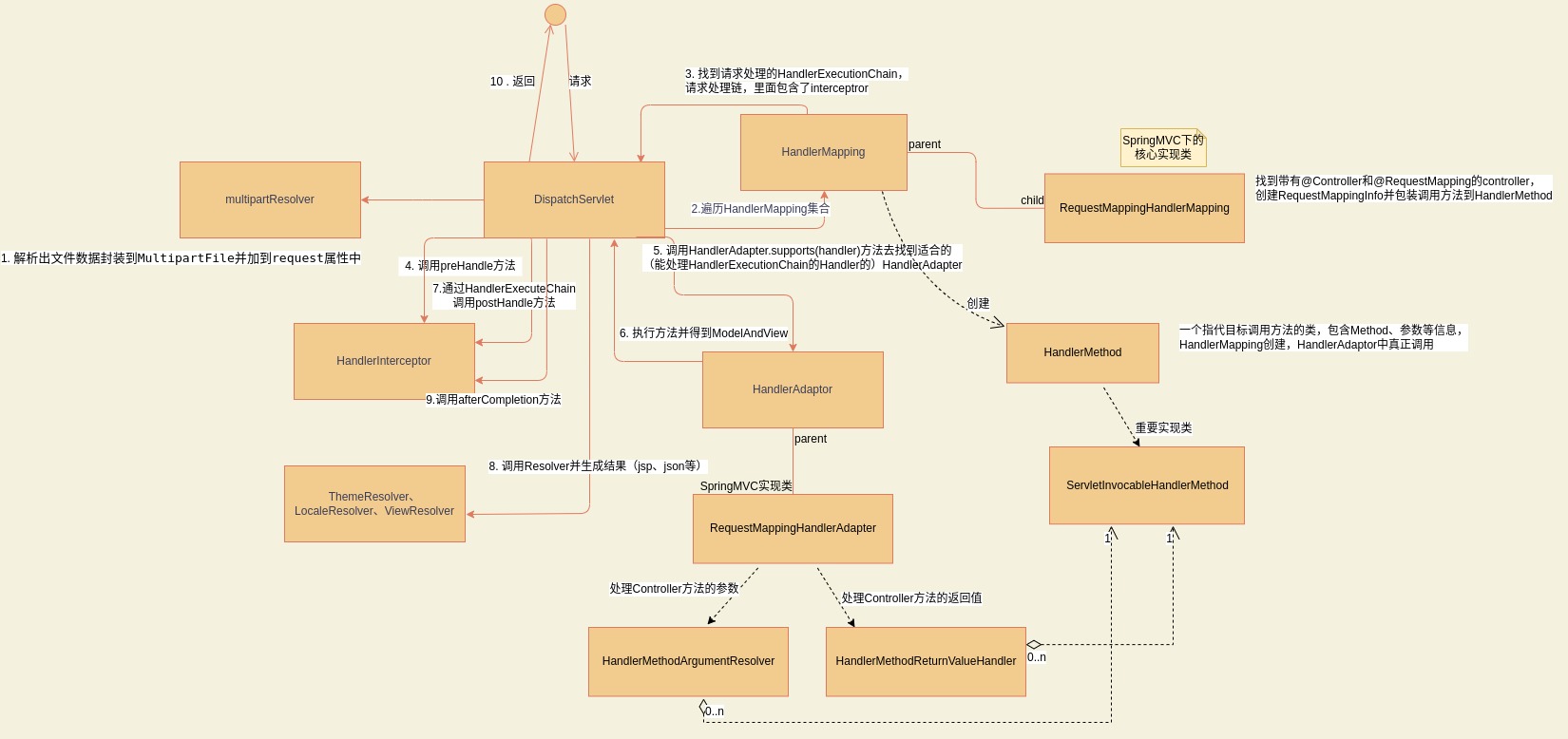
调用关系整理
最终,整理了一下组件的调用关系图。